Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Prediction example#
In this example, we will use the model to predict the tidal elevation on a specific location, like a tide gauge.
Warning
The model employed is an older FES tidal-atlas model due to its significantly smaller size compared to newer models. Do not use it for real applications. You can download the model from the AVISO website.
First, we import the required modules.
from __future__ import annotations
import os
import pathlib
from IPython.display import HTML
import markdown
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy
import pyfes
To display properly formatted markdown tables in this notebook, we define a helper function that converts markdown strings to HTML.
def md_to_html(md_string: str) -> HTML:
"""Convert a markdown string to HTML for display in Jupyter."""
html_string = markdown.markdown(md_string, extensions=['tables'])
return HTML(html_string)
Loading the model configuration#
First we create an environment variable to store the path to the model file.
os.environ['DATASET_DIR'] = str(
pathlib.Path().absolute().parent / 'tests' / 'python' / 'dataset'
)
Now we need to create the instances of the model used to calculate the ocean tide and the radial tide. To do this, we need to create a YAML file that describes the models and their parameters. The configuration file is fully documented in the documentation.
Note
The content of the configuration file is viewable in the GitHub repository.
config = pyfes.config.load(pathlib.Path().absolute() / 'fes_slev.yml')
Hint
By default, the function pyfes.config.load() loads the entire
numeric grid into memory. To predict the tide for a specific region, you
can use the bbox keyword argument to specify the region’s bounding
box. This bounding box is a tuple of four elements: minimum longitude,
minimum latitude, maximum longitude, and maximum latitude. Example:
config = pyfes.config.load('fes_slev.yaml', bbox=(-10, 40, 10, 60))
config is a Configuration namedtuple that
contains the tidal models and the runtime settings loaded from the
configuration file.
print(config)
Configuration(models={'radial': TidalModelInterface(9 constituents, tide_type=RADIAL), 'tide': TidalModelInterface(15 constituents, tide_type=TIDE)}, settings=<FESSettings num_threads=0>)
Prediction Engine Information#
This configuration uses the FES/Darwin engine, which employs Darwin’s harmonic notation with Schureman’s nodal corrections. This is the classical engine designed for FES tidal atlases.
The Darwin engine:
Uses fundamental astronomical arguments (s, h, p, N, p₁)
Applies individual Schureman nodal corrections to each constituent
Supports 99 tidal constituents
Uses traditional admittance for minor constituents
To use the PERTH/Doodson engine instead (for GOT tidal models), set
engine: perth in your YAML configuration. The PERTH engine uses Doodson
number classification and group modulations. See the
engine comparison example for details on
choosing between engines.
print(f'\nRuntime Settings: {type(config.settings).__name__}')
print('Engine: FES/Darwin (Schureman nodal corrections)')
print(f'Astronomical formulae: {config.settings.astronomic_formulae}')
print(f'Time tolerance: {config.settings.time_tolerance} seconds')
Runtime Settings: FESSettings
Engine: FES/Darwin (Schureman nodal corrections)
Astronomical formulae: Formulae.SCHUREMAN_ORDER_1
Time tolerance: 0.0 seconds
Displaying the Configuration as a Markdown Table#
You can generate a markdown table summarizing the engine settings and the
constituent list (modeled vs. inferred) using
pyfes.generate_markdown_table(). Pass the settings and the list
of modeled constituents to see which ones are provided by the atlas and which
ones will be inferred.
md_to_html(
pyfes.generate_markdown_table(
config.settings,
modeled_constituents=config.models['tide'].identifiers(),
)
)
Generating the tide prediction#
Set up the position and the dates where we want to calculate the tide.
lon = -7.688
lat = 59.195
date = numpy.datetime64('1983-01-01T00:00:00')
Generate the coordinates where we want to calculate the tide.
dates = numpy.arange(
date, date + numpy.timedelta64(1, 'D'), numpy.timedelta64(1, 'h')
)
lons = numpy.full(dates.shape, lon)
lats = numpy.full(dates.shape, lat)
We can now calculate the ocean tide and the radial tide.
Displaying the results#
Calculate CNES Julian Days (days since 1950-01-01). This is the standard time reference used in CNES altimetry products.
cnes_julian_days = (dates - numpy.datetime64('1950-01-01T00:00:00')).astype(
'M8[s]'
).astype(float) / 86400
hours = cnes_julian_days % 1 * 24
print(
f'{"JulDay":>6s} {"Hour":>5s} {"Latitude":>10s} {"Longitude":>10s} '
f'{"Short_tide":>10s} {"LP_tide":>10s} {"Pure_Tide":>10s} '
f'{"Geo_Tide":>10s} {"Rad_Tide":>10s}'
)
print('=' * 89)
for ix, jd in enumerate(cnes_julian_days):
print(
f'{jd:>6.0f} {hours[ix]:>5.0f} {lats[ix]:>10.3f} {lons[ix]:>10.3f} '
f'{tide[ix]:>10.3f} {lp[ix]:>10.3f} {tide[ix] + lp[ix]:>10.3f} '
f'{tide[ix] + lp[ix] + load[ix]:>10.3f} {load[ix]:>10.3f}'
)
JulDay Hour Latitude Longitude Short_tide LP_tide Pure_Tide Geo_Tide Rad_Tide
=========================================================================================
12053 0 59.195 -7.688 -100.991 0.896 -100.095 -96.214 3.881
12053 1 59.195 -7.688 -137.105 0.869 -136.236 -131.907 4.328
12053 2 59.195 -7.688 -138.483 0.842 -137.641 -133.930 3.711
12053 3 59.195 -7.688 -104.346 0.814 -103.532 -101.398 2.134
12053 4 59.195 -7.688 -42.516 0.785 -41.731 -41.783 -0.052
12053 5 59.195 -7.688 32.374 0.756 33.130 30.789 -2.341
12053 6 59.195 -7.688 102.167 0.726 102.893 98.699 -4.194
12053 7 59.195 -7.688 149.469 0.696 150.165 144.993 -5.172
12053 8 59.195 -7.688 162.102 0.665 162.767 157.722 -5.046
12053 9 59.195 -7.688 136.505 0.634 137.139 133.287 -3.852
12053 10 59.195 -7.688 78.896 0.602 79.498 77.613 -1.885
12053 11 59.195 -7.688 3.645 0.570 4.215 4.597 0.382
12054 12 59.195 -7.688 -70.659 0.537 -70.121 -67.711 2.411
12054 13 59.195 -7.688 -126.152 0.504 -125.647 -121.914 3.734
12054 14 59.195 -7.688 -150.115 0.471 -149.644 -145.573 4.071
12054 15 59.195 -7.688 -137.779 0.437 -137.342 -133.949 3.393
12054 16 59.195 -7.688 -93.132 0.403 -92.729 -90.801 1.928
12054 17 59.195 -7.688 -27.820 0.369 -27.451 -27.354 0.097
12054 18 59.195 -7.688 41.541 0.334 41.875 40.282 -1.593
12054 19 59.195 -7.688 97.250 0.299 97.549 94.865 -2.684
12054 20 59.195 -7.688 124.939 0.263 125.203 122.321 -2.882
12054 21 59.195 -7.688 117.465 0.228 117.693 115.561 -2.132
12054 22 59.195 -7.688 77.026 0.192 77.218 76.583 -0.635
12054 23 59.195 -7.688 14.661 0.156 14.817 16.027 1.210
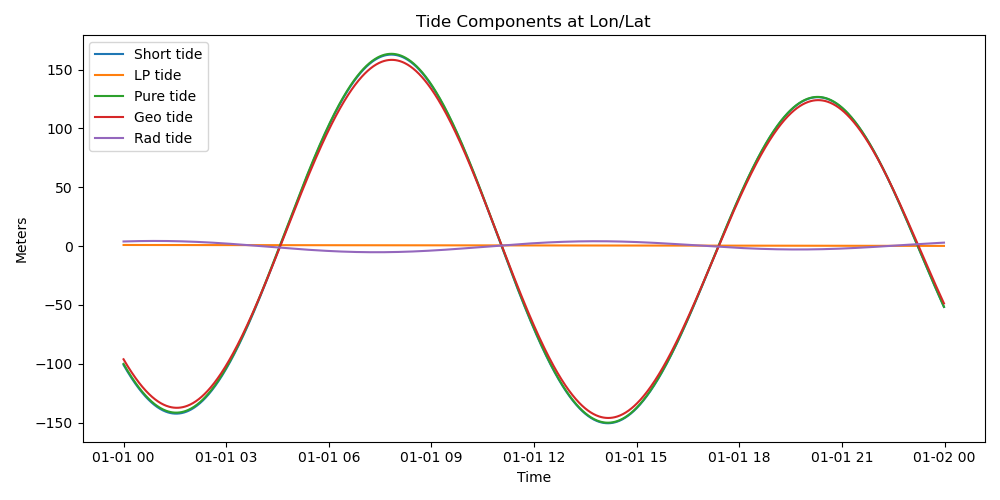
Plot the tide components shown in the table. We recompute the tide only to generate smoother curves on the figure below.
dates = numpy.arange(
date, date + numpy.timedelta64(1, 'D'), numpy.timedelta64(1, 'm')
)
lons = numpy.full(dates.shape, lon)
lats = numpy.full(dates.shape, lat)
tide, lp, _ = pyfes.evaluate_tide(
config.models['tide'], dates, lons, lats, settings=config.settings
)
load, load_lp, _ = pyfes.evaluate_tide(
config.models['radial'], dates, lons, lats, settings=config.settings
)
pure_tide = tide + lp
geo_tide = pure_tide + load
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(dates, tide, label='Short tide')
plt.plot(dates, lp, label='LP tide')
plt.plot(dates, pure_tide, label='Pure tide')
plt.plot(dates, geo_tide, label='Geo tide')
plt.plot(dates, load, label='Rad tide')
plt.title('Tide Components at Lon/Lat')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Meters')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.412 seconds)