Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder.
Spatial Predicates and Relationships#
This example demonstrates the spatial predicates and relationship functions
available in the pyinterp.geometry module. These functions allow you to
query the spatial relationships between geometric objects, which is essential
for spatial analysis and filtering.
Spatial Predicates Covered:
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
Tests if geometry is completely inside another |
|
Tests if geometry is covered by another |
|
Tests if geometries have any intersection |
|
Tests if geometries have no intersection |
|
Tests if geometries cross each other |
|
Tests if geometries touch at boundaries |
|
Tests if geometries overlap |
|
Tests if geometries are spatially equal |
|
Tests using DE-9IM pattern |
|
Gets DE-9IM relationship string |
Vectorized Predicates:
Function |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Test which points are within a geometry |
|
Test which points are covered by a geometry |
|
Calculate distances from points to a geometry |
Let’s start by importing the necessary libraries.
import cartopy.crs
import cartopy.feature
import matplotlib.pyplot
import numpy
from pyinterp.geometry import geographic
Setup: Create Test Geometries#
Let’s create various geometries to test spatial relationships
wgs84 = geographic.Spheroid()
# Create points
point_inside = geographic.Point(2.0, 2.0)
point_on_boundary = geographic.Point(0.0, 2.0)
point_outside = geographic.Point(10.0, 10.0)
# Create a box
box = geographic.Box((0.0, 0.0), (5.0, 5.0))
# Create a polygon
poly_lon = numpy.array([1.0, 1.0, 4.0, 4.0, 1.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
poly_lat = numpy.array([1.0, 4.0, 4.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
polygon = geographic.Polygon(geographic.Ring(poly_lon, poly_lat))
# Create overlapping polygon
overlap_lon = numpy.array([3.0, 3.0, 6.0, 6.0, 3.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
overlap_lat = numpy.array([3.0, 6.0, 6.0, 3.0, 3.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
overlap_poly = geographic.Polygon(geographic.Ring(overlap_lon, overlap_lat))
# Create a line
line_lon = numpy.array([0.0, 5.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
line_lat = numpy.array([2.5, 2.5], dtype=numpy.float64)
line = geographic.LineString(line_lon, line_lat)
# Create a crossing line
cross_lon = numpy.array([2.5, 2.5], dtype=numpy.float64)
cross_lat = numpy.array([0.0, 5.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
cross_line = geographic.LineString(cross_lon, cross_lat)
print("Test geometries created successfully")
Test geometries created successfully
Within: Is Geometry Completely Inside Another?#
The within() predicate
tests if a geometry is completely within another geometry (not touching the
boundary).
print("\nWithin Predicate:")
print(
" point_inside within box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.within(point_inside, box)}"
)
print(
f" point_on_boundary within box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.within(point_on_boundary, box)}"
)
print(
f" point_outside within box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.within(point_outside, box)}"
)
box_as_poly = geographic.Polygon(
geographic.Ring(
numpy.array(
[
box.min_corner.lon,
box.max_corner.lon,
box.max_corner.lon,
box.min_corner.lon,
box.min_corner.lon,
],
dtype=numpy.float64,
),
numpy.array(
[
box.min_corner.lat,
box.min_corner.lat,
box.max_corner.lat,
box.max_corner.lat,
box.min_corner.lat,
],
dtype=numpy.float64,
),
)
)
print(
" polygon within box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.within(polygon, box_as_poly)}"
)
print(
f" overlap_poly within box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.within(overlap_poly, box_as_poly)}"
)
Within Predicate:
point_inside within box: True
point_on_boundary within box: False
point_outside within box: False
polygon within box: True
overlap_poly within box: False
Covered By: Is Geometry Covered By Another?#
The covered_by() predicate
is similar to within, but allows the geometry to touch the boundary.
print("\nCovered By Predicate:")
print(
f" point_inside covered_by box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.covered_by(point_inside, box)}"
)
print(
f" point_on_boundary covered_by box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.covered_by(point_on_boundary, box)}"
)
print(
f" point_outside covered_by box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.covered_by(point_outside, box)}"
)
print(
f" polygon covered_by box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.covered_by(polygon, box)}"
)
Covered By Predicate:
point_inside covered_by box: True
point_on_boundary covered_by box: True
point_outside covered_by box: False
polygon covered_by box: True
Intersects: Do Geometries Have Any Intersection?#
The intersects() predicate
tests if geometries have any point in common.
print("\nIntersects Predicate:")
print(
f" point_inside intersects box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.intersects(point_inside, box)}"
)
print(
f" point_outside intersects box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.intersects(point_outside, box)}"
)
print(
f" polygon intersects overlap_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.intersects(polygon, overlap_poly)}"
)
print(f" line intersects box: {geographic.algorithms.intersects(line, box)}")
print(
f" line intersects cross_line: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.intersects(line, cross_line)}"
)
Intersects Predicate:
point_inside intersects box: True
point_outside intersects box: False
polygon intersects overlap_poly: True
line intersects box: True
line intersects cross_line: True
Disjoint: Do Geometries Have No Intersection?#
The disjoint() predicate
is the opposite of intersects.
print("\nDisjoint Predicate:")
print(
f" point_inside disjoint box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.disjoint(point_inside, box)}"
)
print(
f" point_outside disjoint box: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.disjoint(point_outside, box)}"
)
print(
f" polygon disjoint overlap_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.disjoint(polygon, overlap_poly)}"
)
# Verify: intersects and disjoint should be opposites
intersects_result = geographic.algorithms.intersects(point_outside, box)
disjoint_result = geographic.algorithms.disjoint(point_outside, box)
print(
f" Verification: intersects={intersects_result}, "
f"disjoint={disjoint_result}, "
f"opposite={intersects_result != disjoint_result}"
)
Disjoint Predicate:
point_inside disjoint box: False
point_outside disjoint box: True
polygon disjoint overlap_poly: False
Verification: intersects=False, disjoint=True, opposite=True
Crosses: Do Geometries Cross Each Other?#
The crosses() predicate
tests if geometries cross each other (share some but not all interior points).
print("\nCrosses Predicate:")
print(
f" line crosses polygon: {geographic.algorithms.crosses(line, polygon)}"
)
print(
f" cross_line crosses polygon: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.crosses(cross_line, polygon)}"
)
print(
f" line crosses cross_line: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.crosses(line, cross_line)}"
)
Crosses Predicate:
line crosses polygon: True
cross_line crosses polygon: True
line crosses cross_line: True
Touches: Do Geometries Touch at Boundaries?#
The touches() predicate
tests if geometries touch at their boundaries but don’t overlap interiors.
# Create touching geometries
touch_poly_lon = numpy.array([5.0, 5.0, 8.0, 8.0, 5.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
touch_poly_lat = numpy.array([1.0, 4.0, 4.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
touch_poly = geographic.Polygon(
geographic.Ring(touch_poly_lon, touch_poly_lat)
)
# Create a point on the polygon boundary
boundary_point = geographic.Point(1.0, 2.5)
print("\nTouches Predicate:")
print(
f" polygon touches touch_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.touches(polygon, touch_poly)}"
)
print(
f" polygon touches overlap_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.touches(polygon, overlap_poly)}"
)
print(
f" boundary_point touches polygon: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.touches(boundary_point, polygon)}"
)
Touches Predicate:
polygon touches touch_poly: False
polygon touches overlap_poly: False
boundary_point touches polygon: True
Overlaps: Do Geometries Overlap?#
The overlaps() predicate
tests if geometries overlap (share some but not all space, and have the same
dimension).
print("\nOverlaps Predicate:")
print(
f" polygon overlaps overlap_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.overlaps(polygon, overlap_poly)}"
)
print(
f" polygon overlaps touch_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.overlaps(polygon, touch_poly)}"
)
print(
" line overlaps cross_line: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.overlaps(line, cross_line)}"
)
Overlaps Predicate:
polygon overlaps overlap_poly: True
polygon overlaps touch_poly: False
line overlaps cross_line: False
Equals: Are Geometries Spatially Equal?#
The equals() predicate
tests if geometries represent the same spatial object.
# Create identical polygons
poly1 = polygon
poly2_lon = numpy.array([1.0, 1.0, 4.0, 4.0, 1.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
poly2_lat = numpy.array([1.0, 4.0, 4.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=numpy.float64)
poly2 = geographic.Polygon(geographic.Ring(poly2_lon, poly2_lat))
print("\nEquals Predicate:")
print(f" polygon equals poly2: {geographic.algorithms.equals(poly1, poly2)}")
print(
f" polygon equals overlap_poly: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.equals(polygon, overlap_poly)}"
)
Equals Predicate:
polygon equals poly2: True
polygon equals overlap_poly: False
Relate and Relation: DE-9IM Pattern Matching#
The DE-9IM (Dimensionally Extended 9-Intersection Model) provides a detailed way to describe spatial relationships.
# Get the relationship string
relation_str = geographic.algorithms.relation(polygon, overlap_poly)
print(f"\nDE-9IM Relationship (polygon vs overlap_poly): {relation_str}")
# Test specific patterns
# "T********" means interiors intersect
print(
f" Interiors intersect: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.relate(polygon, overlap_poly, 'T********')}"
)
# "****T****" means boundaries intersect
print(
f" Boundaries intersect: "
f"{geographic.algorithms.relate(polygon, overlap_poly, '****T****')}"
)
DE-9IM Relationship (polygon vs overlap_poly): 212101212
Interiors intersect: True
Boundaries intersect: True
Distance: Calculating Distances Between Geometries#
While not a boolean predicate, distance calculations are closely related to spatial relationships.
print("\nDistance Calculations:")
dist_to_inside = geographic.algorithms.distance(
point_inside, polygon, spheroid=wgs84
)
dist_to_outside = geographic.algorithms.distance(
point_outside, polygon, spheroid=wgs84
)
dist_to_boundary = geographic.algorithms.distance(
boundary_point, polygon, spheroid=wgs84
)
print(f" Distance from point_inside to polygon: {dist_to_inside:.2f} m")
print(
f" Distance from point_outside to polygon: {dist_to_outside * 1e-3:.2f} km"
)
print(f" Distance from boundary_point to polygon: {dist_to_boundary:.2f} m")
# Distance between polygons
poly_dist = geographic.algorithms.distance(
polygon, overlap_poly, spheroid=wgs84
)
print(f" Distance between polygon and overlap_poly: {poly_dist:.2f} m")
Distance Calculations:
Distance from point_inside to polygon: 0.00 m
Distance from point_outside to polygon: 937.76 km
Distance from boundary_point to polygon: 0.00 m
Distance between polygon and overlap_poly: 0.00 m
Vectorized Predicates: Testing Multiple Points#
The vectorized predicates allow efficient testing of many points at once.
# Create a grid of points
lon_grid = numpy.arange(-2, 8, 0.5, dtype=numpy.float64)
lat_grid = numpy.arange(-2, 8, 0.5, dtype=numpy.float64)
mx, my = numpy.meshgrid(lon_grid, lat_grid)
grid_points = geographic.MultiPoint(mx.ravel(), my.ravel())
# Test which points are within the polygon
mask_within = geographic.algorithms.for_each_point_within(grid_points, polygon)
mask_covered = geographic.algorithms.for_each_point_covered_by(
grid_points, polygon
)
print("\nVectorized Predicates on Grid:")
print(f" Total points: {len(grid_points)}")
print(f" Points within polygon: {mask_within.sum()}")
print(f" Points covered by polygon: {mask_covered.sum()}")
print(
f" Difference: {mask_covered.sum() - mask_within.sum()} (boundary points)"
)
Vectorized Predicates on Grid:
Total points: 400
Points within polygon: 30
Points covered by polygon: 44
Difference: 14 (boundary points)
Calculate distances from all points to the polygon
Distance Statistics:
Min distance: 0.00 m
Max distance: 547.76 km
Mean distance: 227.49 km
Real-World Example: Point-in-Polygon for Gulf of Mexico#
This is a practical example of using spatial predicates for geographic selection.
gulf_lon = numpy.array(
[-97.5, -97.5, -82.5, -82.5, -90.0, -97.5], dtype=numpy.float64
)
gulf_lat = numpy.array(
[20.0, 30.0, 30.0, 20.0, 17.5, 20.0], dtype=numpy.float64
)
gulf_of_mexico = geographic.Polygon(geographic.Ring(gulf_lon, gulf_lat))
# Create observation points
obs_lon = numpy.arange(-100, -80, 2, dtype=numpy.float64)
obs_lat = numpy.arange(15, 35, 2, dtype=numpy.float64)
obs_mx, obs_my = numpy.meshgrid(obs_lon, obs_lat)
observations = geographic.MultiPoint(obs_mx.ravel(), obs_my.ravel())
# Filter points
mask_in_gulf = geographic.algorithms.for_each_point_covered_by(
observations, gulf_of_mexico
)
distances_to_gulf = geographic.algorithms.for_each_point_distance(
observations, gulf_of_mexico, spheroid=wgs84
)
print("\nGulf of Mexico Analysis:")
print(f" Total observation points: {len(observations)}")
print(f" Points in Gulf: {mask_in_gulf.sum()}")
print(f" Points outside Gulf: {(~mask_in_gulf).sum()}")
print(f" Max distance to Gulf: {distances_to_gulf.max() * 1e-3:.2f} km")
Gulf of Mexico Analysis:
Total observation points: 100
Points in Gulf: 40
Points outside Gulf: 60
Max distance to Gulf: 613.72 km
Visualization: Spatial Predicates in Action#
fig = matplotlib.pyplot.figure(figsize=(16, 12))
# Plot 1: Basic Predicates (Within, Covered By, Intersects)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 1)
box_corners = [
[box.min_corner.lon, box.min_corner.lat],
[box.max_corner.lon, box.min_corner.lat],
[box.max_corner.lon, box.max_corner.lat],
[box.min_corner.lon, box.max_corner.lat],
]
box_poly = matplotlib.pyplot.Polygon(
box_corners, fill=False, edgecolor="black", linewidth=2, label="Box"
)
ax1.add_patch(box_poly)
ax1.plot(
point_inside.lon,
point_inside.lat,
"go",
markersize=10,
label="Inside (within+covered)",
)
ax1.plot(
point_on_boundary.lon,
point_on_boundary.lat,
"yo",
markersize=10,
label="Boundary (covered only)",
)
ax1.plot(
point_outside.lon,
point_outside.lat,
"ro",
markersize=10,
label="Outside (disjoint)",
)
ax1.set_xlim(-2, 12)
ax1.set_ylim(-2, 12)
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax1.legend()
ax1.set_title("Within, Covered By, Intersects")
ax1.set_xlabel("Longitude")
ax1.set_ylabel("Latitude")
# Plot 2: Overlaps and Touches
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 2)
ax2.fill(poly_lon, poly_lat, alpha=0.3, color="blue", label="Polygon")
ax2.plot(poly_lon, poly_lat, "b-", linewidth=2)
ax2.fill(
overlap_lon, overlap_lat, alpha=0.3, color="red", label="Overlap Polygon"
)
ax2.plot(overlap_lon, overlap_lat, "r-", linewidth=2)
ax2.fill(
touch_poly_lon,
touch_poly_lat,
alpha=0.3,
color="green",
label="Touch Polygon",
)
ax2.plot(touch_poly_lon, touch_poly_lat, "g-", linewidth=2)
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax2.legend()
ax2.set_title("Overlaps vs Touches")
ax2.set_xlabel("Longitude")
ax2.set_ylabel("Latitude")
# Plot 3: Crosses
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 3)
ax3.fill(poly_lon, poly_lat, alpha=0.3, color="blue", label="Polygon")
ax3.plot(poly_lon, poly_lat, "b-", linewidth=2)
ax3.plot(
[pt.lon for pt in line],
[pt.lat for pt in line],
"r-",
linewidth=2,
label="Horizontal Line",
)
ax3.plot(
[pt.lon for pt in cross_line],
[pt.lat for pt in cross_line],
"g-",
linewidth=2,
label="Vertical Line",
)
ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax3.legend()
ax3.set_title("Crosses")
ax3.set_xlabel("Longitude")
ax3.set_ylabel("Latitude")
# Plot 4: Vectorized Predicates (Grid)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 4)
mask_within_2d = mask_within.reshape(mx.shape)
mask_covered_2d = mask_covered.reshape(mx.shape)
ax4.scatter(
mx[mask_within_2d],
my[mask_within_2d],
c="green",
s=30,
label="Within",
alpha=0.6,
)
boundary_mask = mask_covered_2d & ~mask_within_2d
ax4.scatter(
mx[boundary_mask],
my[boundary_mask],
c="yellow",
s=50,
marker="s",
label="On Boundary",
alpha=0.8,
)
ax4.scatter(
mx[~mask_covered_2d],
my[~mask_covered_2d],
c="red",
s=20,
label="Outside",
alpha=0.3,
)
ax4.fill(poly_lon, poly_lat, fill=False, edgecolor="blue", linewidth=2)
ax4.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax4.legend()
ax4.set_title("Vectorized Predicates")
ax4.set_xlabel("Longitude")
ax4.set_ylabel("Latitude")
# Plot 5: Distance Field
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 5)
distances_2d = distances.reshape(mx.shape)
contour = ax5.contourf(mx, my, distances_2d * 1e-3, levels=20, cmap="viridis")
ax5.fill(poly_lon, poly_lat, fill=False, edgecolor="red", linewidth=2)
cbar = matplotlib.pyplot.colorbar(contour, ax=ax5)
cbar.set_label("Distance (km)")
ax5.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax5.set_title("Distance Field to Polygon")
ax5.set_xlabel("Longitude")
ax5.set_ylabel("Latitude")
# Plot 6: Gulf of Mexico Example
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(2, 3, 6, projection=cartopy.crs.PlateCarree())
ax6.add_feature(cartopy.feature.LAND)
ax6.add_feature(cartopy.feature.OCEAN)
ax6.add_feature(cartopy.feature.COASTLINE)
ax6.gridlines(draw_labels=True, dms=True, x_inline=False, y_inline=False)
ax6.set_extent([-100, -80, 15, 35])
# Plot Gulf boundary
ax6.plot(
gulf_lon,
gulf_lat,
color="red",
linewidth=2,
transform=cartopy.crs.Geodetic(),
label="Gulf of Mexico",
)
# Plot observation points
mask_2d = mask_in_gulf.reshape(obs_mx.shape)
ax6.scatter(
obs_mx[mask_2d],
obs_my[mask_2d],
color="green",
s=50,
label="In Gulf",
transform=cartopy.crs.PlateCarree(),
zorder=3,
)
ax6.scatter(
obs_mx[~mask_2d],
obs_my[~mask_2d],
color="gray",
s=20,
label="Outside",
transform=cartopy.crs.PlateCarree(),
alpha=0.5,
)
ax6.legend()
ax6.set_title("Gulf of Mexico Selection")
matplotlib.pyplot.tight_layout()
matplotlib.pyplot.suptitle(
"Spatial Predicates and Relationships",
fontsize=16,
fontweight="bold",
y=1.00,
)
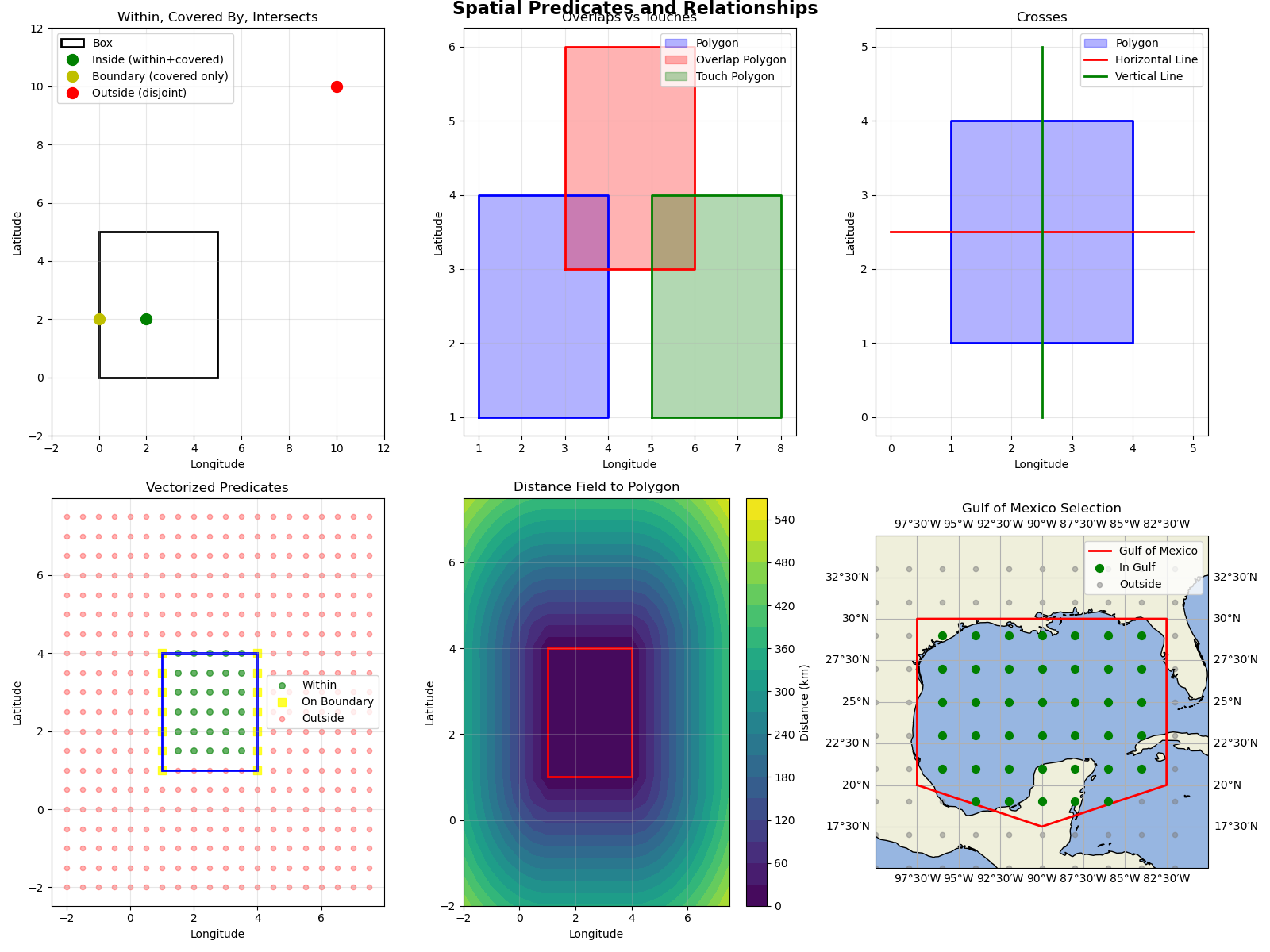
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Spatial Predicates and Relationships')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.503 seconds)