 |
EleFits
4.0.0
A modern C++ API on top of CFitsIO
|
 |
EleFits
4.0.0
A modern C++ API on top of CFitsIO
|
All the services you need!
EleFits is split into service classes, known as handlers, in the package EleFits, and data classes in EleFitsData.
File handlers (MefFile and SifFile) store the index and type of the HDUs, access and create HDUs. HDU handlers (Hdu, ImageHdu, BintableHdu, Header, ImageRaster, BintableColumns and BintableRows) only provide read/write services. Records, images and tables are never stored by those classes (to know where they are, refer to Data classes). Instead, when you access an HDU, you just access a set of services to read and write items in this HDU.
FitsFile is mostly en empty shell for opening and closing operations. You could instantiate and destroy a FitsFile: this would just create a file with empty Primary, and not even give you access to it! Services of iterest lie in the MefFile and SifFile classes, which both extend FitsFile. This is why it is important to know the FitsFile behavior described above: When you instantiate a MefFile or SifFile, the Primary HDU is initialized with an empty image. This means:
The rationale is that a FitsFile should always represent a valid Fits file, and therefore have at the minimum one image HDU with all the mandatory keyword records.
Multi-extension Fits (MEF) files are manipulated through the MefFile class.
All in all, MefFile is a mere container of HDUs, each of which is either of type ImageHdu or BintableHdu. There are methods to access the HDUs by index or by name, to select and iterate over HDUs, and to create new HDUs. Classes ImageHdu and BintableHdu extend Hdu, a parent class which implements the common services. The header units are manipulated by Header objects. The data units of image and binary table HDUs are respectively manipulated by ImageRaster and BintableColumns or BintableRows objects.
Conceptually, MefFile is a tree of objects, which can be minimalistically represented as follows (there are actually many more methods available):
MefFile services:
ImageHdus and BintableHdusImageHdu services:
HeaderImageRasterBintableHdu services:
HeaderBintableColumnsBintableRowsMefFile provides creation methods of two kinds:
init-prefixed methods just fill the header unit of a new HDU with the mandatory keyword records;assign-prefixed methods additionally write the data unit.HDU access and creation methods all return a constant reference to the desired type of HDU: Hdu, ImageHdu or BintableHdu. The header units are read and written through Hdu::header() (also available in ImageHdu and BintableHdu as child classes of Hdu). The data unit handler of image HDUs (ImageRaster) is instantiated by ImageHdu::array(), while those of binary table HDUs (BintableColumns and BintableRows) are instantiated by BintableHdu::columns() and BintableHdu::rows().
All of this is represented in the following class diagram. Again, many services are hidden for the sake of synthesis.
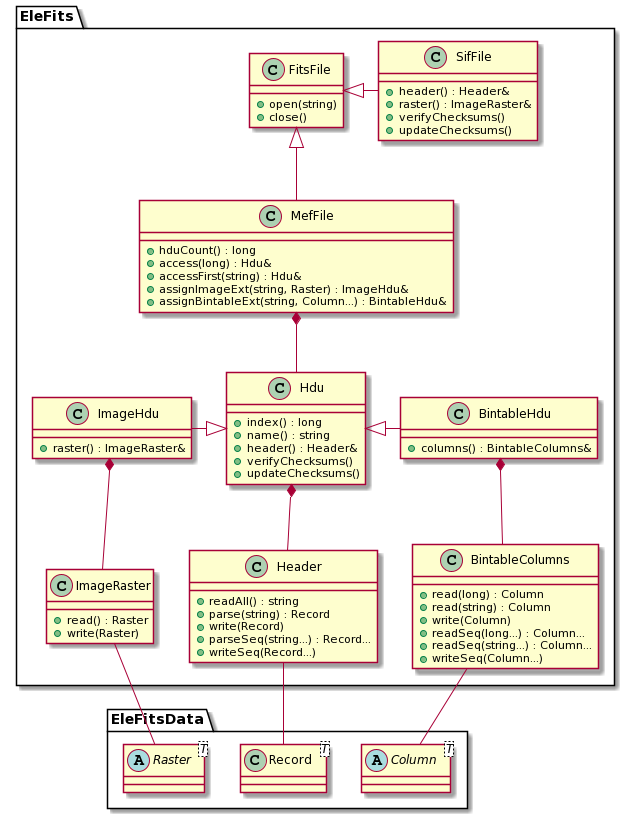
Although they can be seen as simplistic instances of a MEF file, single image Fits (SIF) files have specificities which deserve a dedicated class: SifFile. Shortcuts are provided to read and write the image data, and to access directly the header unit. Of course, it is possible to effectively handle a SIF file with a MefFile object, but this is more verbose, and does not enforce or guarantee that the file is and remains a SIF.
For comparison with MefFile, here is are much simplified tree view and class diagram of SifFile:
SifFile services:
HeaderImageRasterThe organization of the service classes matches that of a Fits file:
All of the classes presented above only provide services to read and write data. The classes which own the said data are presended in Data classes.
Modules | |
| File handlers | |
| Work with the Fits file structure. | |
| HDU selectors and iterators | |
| Tools to iterate over HDUs with selected categories and/or states. | |
| Header unit handlers | |
| Read and write header units. | |
| Image data unit handlers | |
| Read and write image HDUs. | |
| Binary table data unit handlers | |
| Read and write binary table HDUs. | |